Historical Long-Term Sediment Dynamics through Big Data Analysis
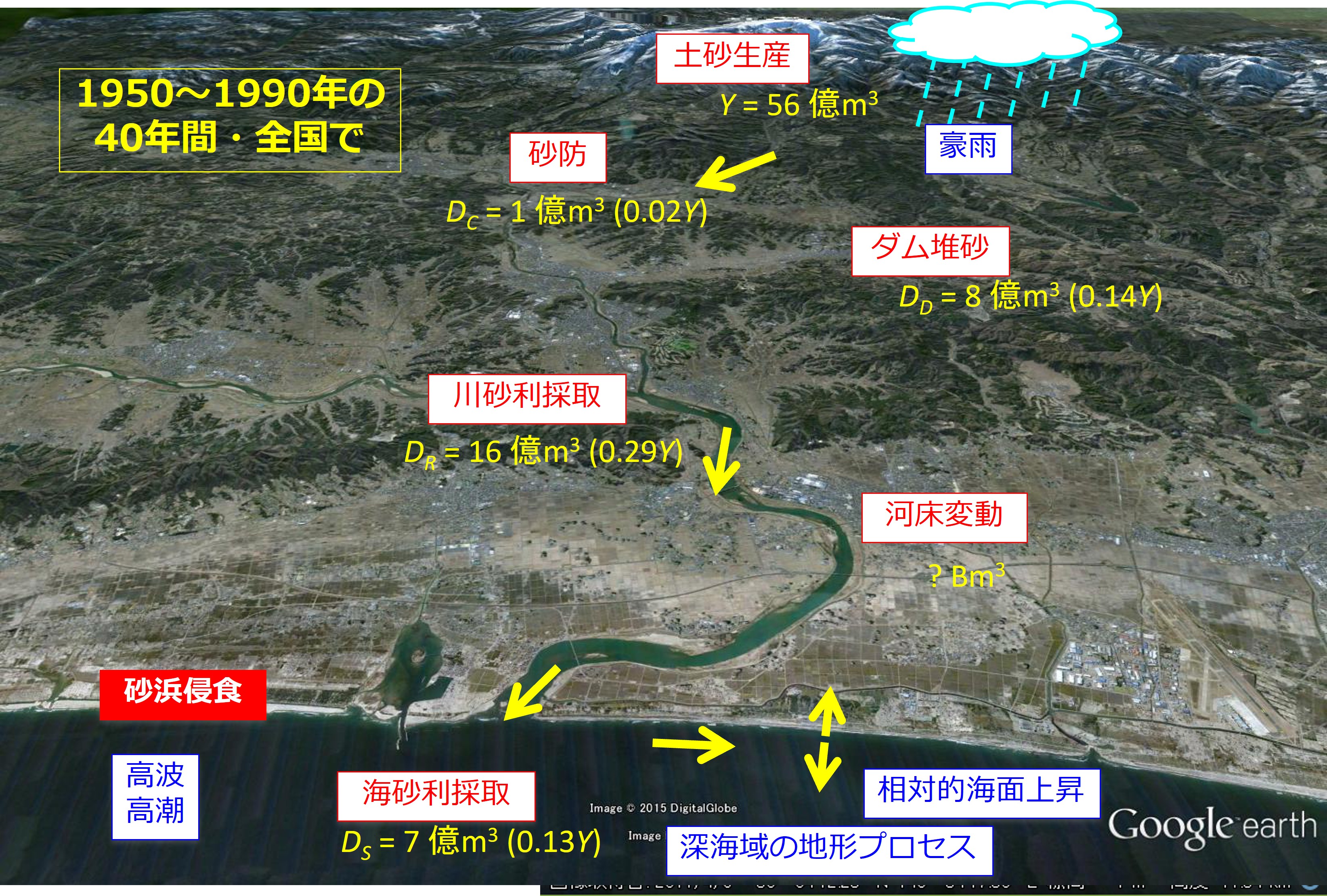
Sediment supplied from mountains to rivers and from rivers to the sea has shaped the land for hundreds and thousands of years. However, during Japan's modernization after the Meiji Era, postwar reconstruction, and rapid economic growth, the supply of sediment was interrupted by human interventions such as erosion control projects to prevent sediment-related disasters, dam construction for flood control and water utilization, and port construction, resulting in sedimentation and erosion problems on rivers and coasts. While these developments had contributed greatly to the construction of a safe, secure, and comfortable infrastructure for our lives, it has also contributed to new problems, and many issues remain to be solved. We are engaged in research to elucidate sediment dynamics by analyzing big data such as national land information and meteorological information.
Estimation of Nationwide Sediment Erosion Volume during Heavy Rainfall Events
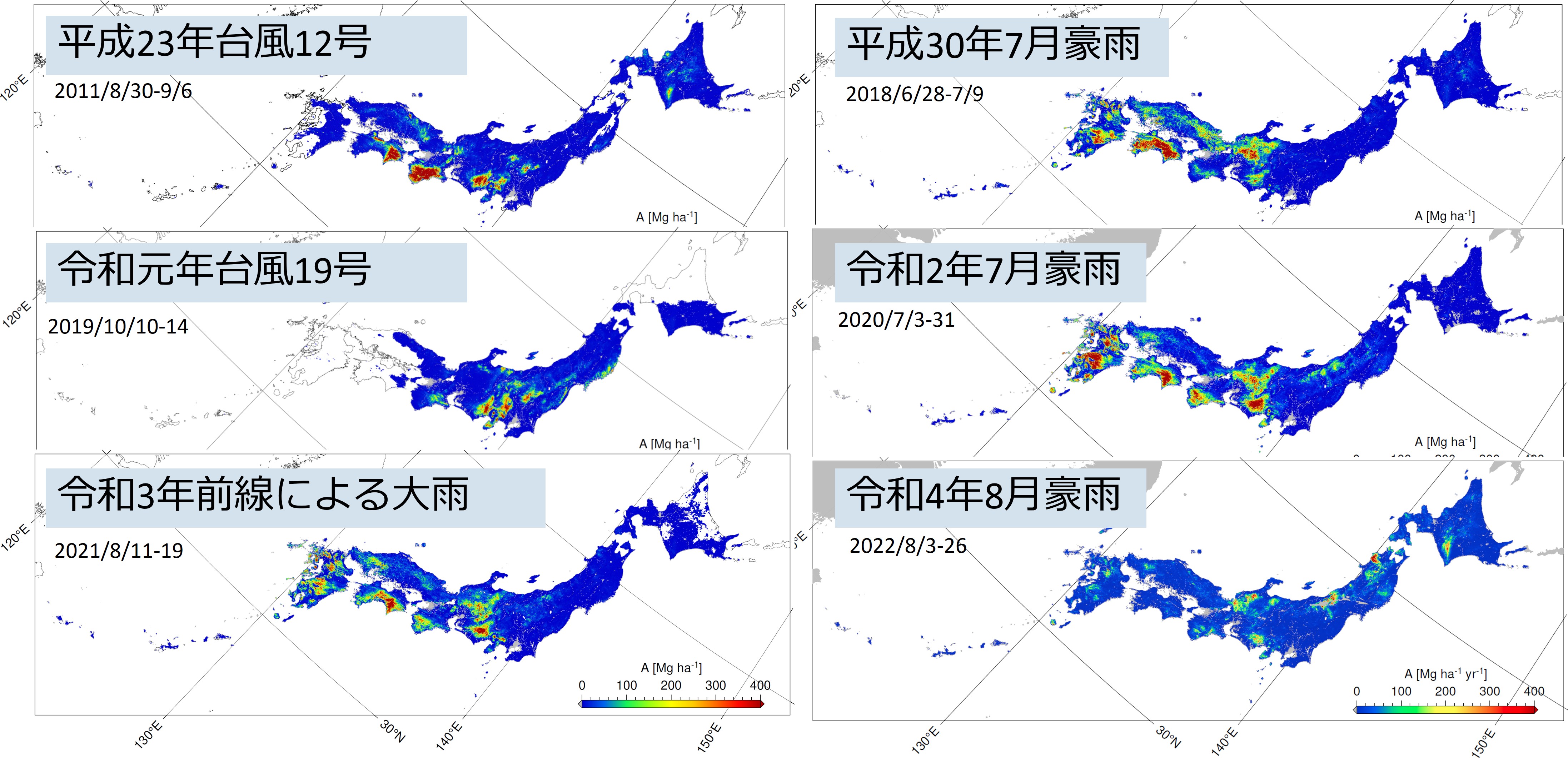
The frequency of heavy rainfall has been increasing in recent years, and as the frequency of heavy rainfall increases, the amount of sediment erosion also increases, affecting the sediment dynamics from the mountains to the sea. By developing a simulation technique to estimate the amount of sediment erosion in a nationwide scale, we aim to contribute to the rapid detection of disaster-damaged area and the projection of the effects of climate change on future sediment erosion dynamics.
Prediction of Future Beach Loss
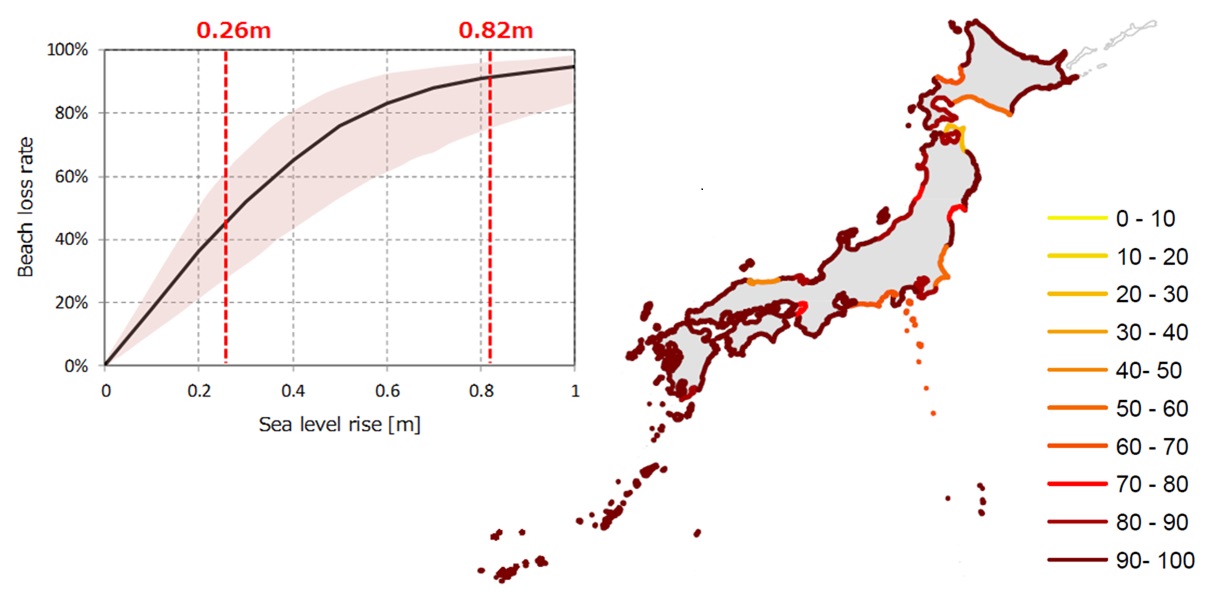
Because beach is already seriously eroded in Japan, there are places where the future rate of beach loss exceeds 80%, even with a rise in sea level of several tens of centimeters. The beach function for disaster mitigation, ecosystem base, and recreation and other uses is lost, depending on the degree of loss. The sandy beache losses due to sea level rise is a global and long-term phenomenon, and similar assessments have been made in Thailand, Egypt, China, and other countries. We are engaged in research on the development of long-term beach models and economic evaluation of sandy beaches to consider better adaptation measures to possible future impacts. You can find the climate change projections including our results in Adaptation Platform for Climate Change Adaptation (A-PLAT).
Evaluation of Sandy Beach Tourism Value Using Hedonic Method
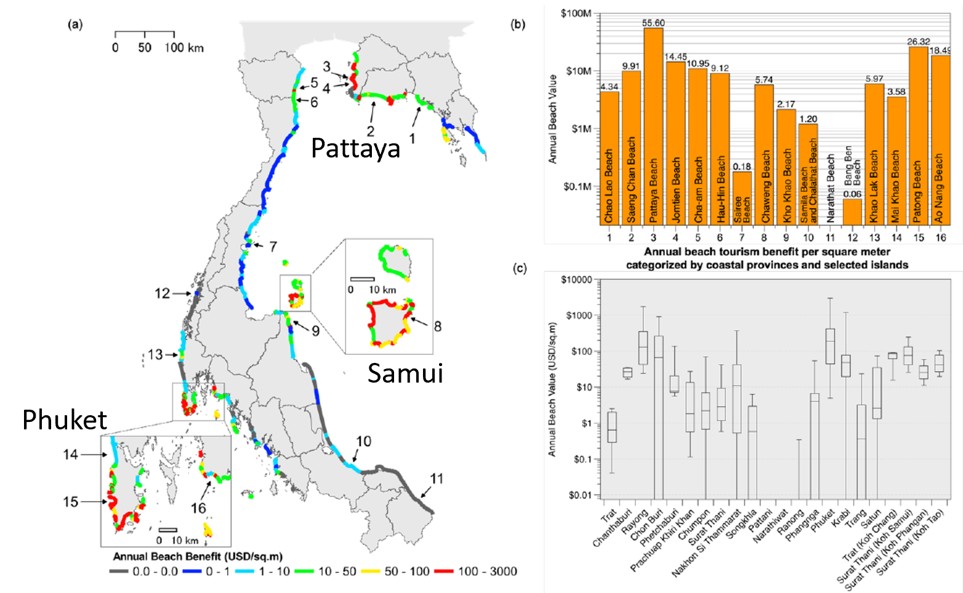
In Thailand, beach resort development is being actively conducted, and the maintenance of sandy beaches is economically important. The serious impact of sea level rise on sandy beaches in Thailand is projected to be similar to that in Japan, and we are studying adaptation measures to this by conducting an economic evaluation. The figure shows the effect of the presence of sandy beaches on the room charge of hotels located on the coast of Thailand estimated by the hedonic method. A similar analysis was performed to evaluate the value of sandy beaches in Japan, but the resort development situation was completely different from Thailand, and it was difficult to evaluate outside of Okinawa (Kayanuma and Udo, 2023). We are studying the beach values that differ from region to region by various methods.
Analysis of Sandy Beach Use using Mobile Spatial Statistics
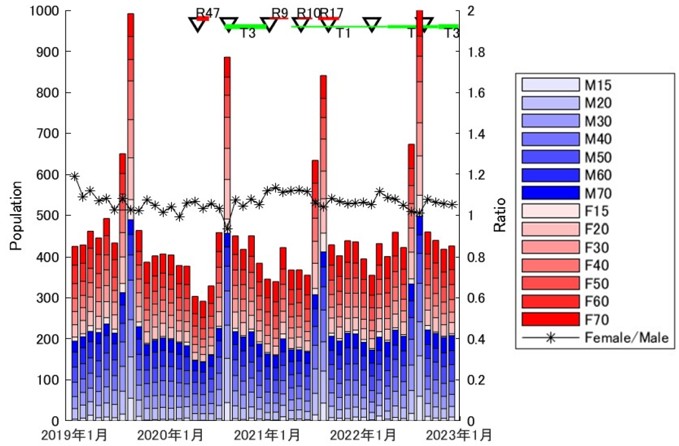
What kind of sandy beach space is desired by people? Every year as summer approaches, there are many news reports about sea turtles, beach daisies, beach cleanups, and so on. Sandy beaches have a function as a place for recreation and others, while at the same time nurturing a rich ecosystem, but the actual situation of how the space is used is not clear. We are conducting an analysis of beach use with the demographic information of cell phones on sandy beaches nationwide (Mobile spatial statistics of DOCOMO InsightMarketing, INC.). By examining the relationship between this demographic and land, weather, and social information, we are studying the desirable management method considering future adaptation.
Articles
- 気候変動により消えゆく白砂青松 ~2100年の日本の砂浜はいかに~
- Loss of storied beach offers cautionary tale for rest of world
- Tune: Keiko Udo (Interview)



